Why Resistance to Change Makes Bitcoin Your Company’s Greatest Asset?
In an era where rapid technological changes often disrupt business strategies, Bitcoin’s resistance to change emerges as a paradoxical advantage for corporate treasuries.
Unlike traditional assets or competing digital currencies, Bitcoin’s governance structure intentionally makes protocol modifications difficult, offering companies a rare combination of technological innovation and operational stability.
The Power of Predictability
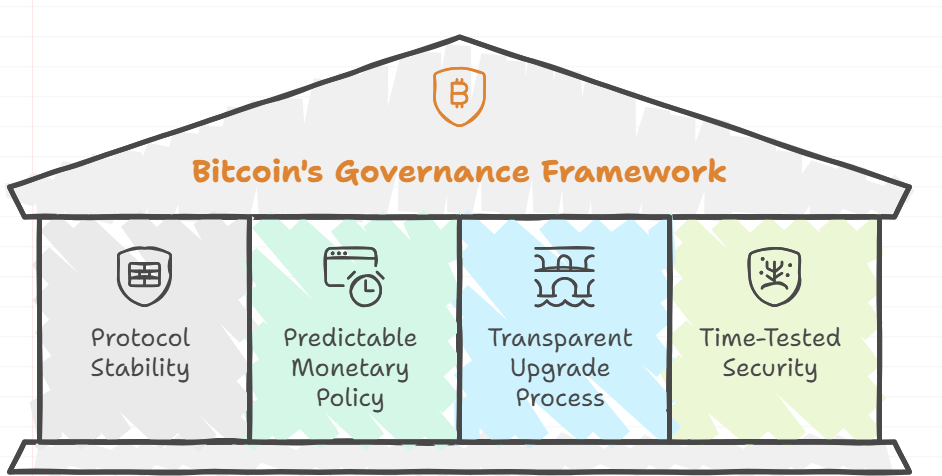
Bitcoin’s governance framework stands apart in the fast-moving digital asset space for these key reasons:
· Protocol Stability: Major changes require overwhelming consensus across the network. This protects against sudden protocol alterations.
· Predictable monetary policy: Fixed supply and predetermined issuance schedule.
· Transparent upgrade process: All proposed changes are publicly discussed and vetted.
· Time-Tested Security: The core protocol has remained robust through multiple market cycles.
Decentralized Decision-Making
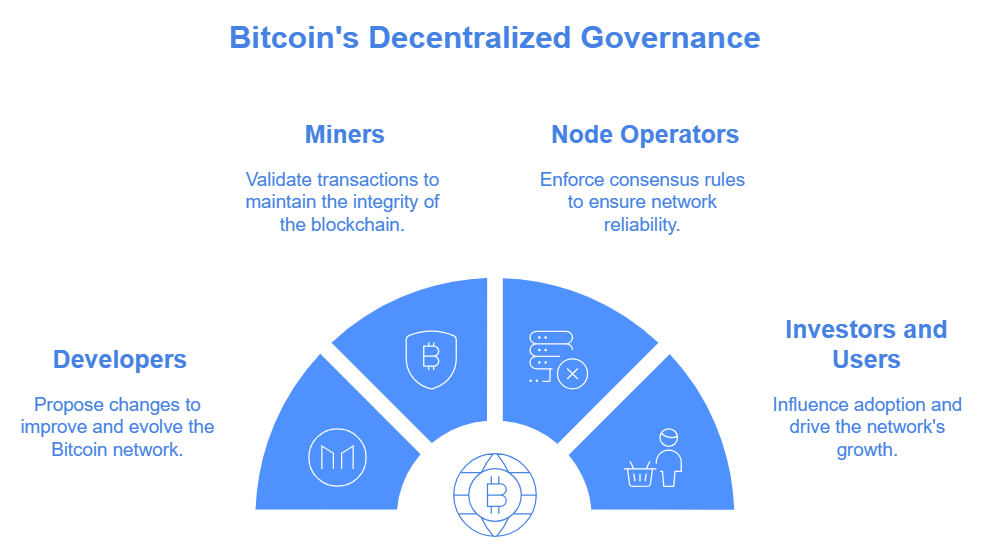
Unlike traditional corporate structures, Bitcoin’s governance is decentralized, involving multiple stakeholders:
· Developers proposing changes
· Miners validating transactions
· Node operators enforcing consensus rules
· Investors and users influencing adoption
This decentralized approach means that no single entity can unilaterally alter the Bitcoin network, providing a level of stability and security that businesses must consider.
Implications for Business Strategy
Long-Term Planning
· Stability: Changes to Bitcoin are intentionally difficult to implement, reducing the risk of sudden, disruptive alterations. This allows businesses to make long-term plans with more confidence.
· Predictability: The open nature of Bitcoin’s decision-making process enables companies to anticipate potential changes and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Risk Management
· Resilience: Bitcoin’s decentralized governance makes it resistant to manipulation by any single party, potentially reducing certain types of financial risks.
· Regulatory Considerations: The lack of a central authority complicates regulatory compliance, requiring businesses to stay informed about evolving legal frameworks across different jurisdictions.
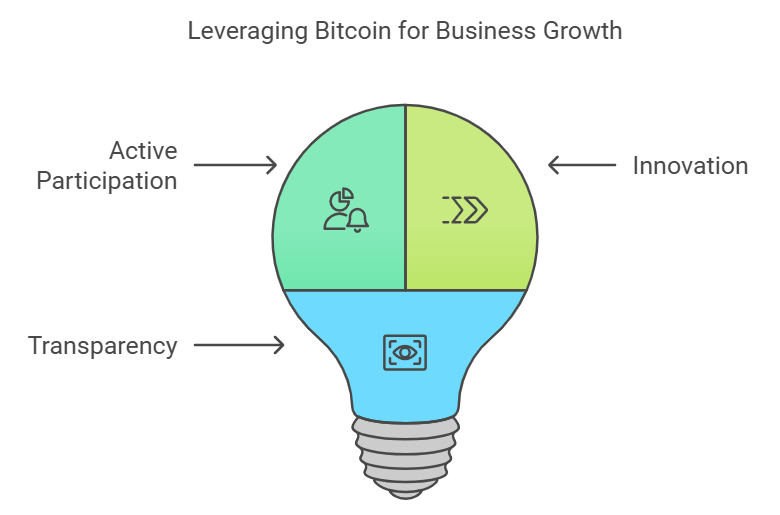
Strategic Opportunities
· Active Participation: Companies heavily invested in Bitcoin can potentially influence its direction by actively engaging in the governance process, such as running nodes or contributing to development.
· Innovation: Bitcoin’s open-source nature allows businesses to build new products and services on top of the network, fostering innovation.
· Transparency: The public nature of Bitcoin’s blockchain provides unprecedented transparency, which can be leveraged for supply chain management or financial reporting.
References for Further Reading
Bitcoin Consensus Analysis Podcast — Discusses the complexities of Bitcoin consensus and stakeholder dynamics.
Navigating Bitcoin’s Future Consensus Risks — Explores the implications of institutional influence on Bitcoin’s governance.
An Empirical Study on Governance in Bitcoin’s Consensus Evolution — Analyzes governance structures in Bitcoin and their impact on decision-making.
Bitcoin Price Prediction Insights — Discusses market factors affecting Bitcoin’s future price trajectory.
Analyzing Bitcoin Consensus: Risks in Protocol Upgrades — This resource provides a detailed analysis of Bitcoin’s consensus mechanism, focusing on the roles of various stakeholders and the risks associated with protocol upgrades.